Recombinant Human β-Galactosidase/GLB1
| Product name: | Recombinant Human β-Galactosidase/GLB1 |
| Source: | Human Cells |
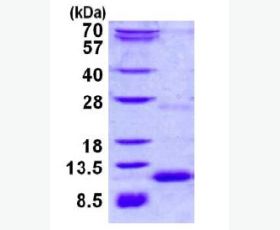
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human beta-Galactosidase is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Leu24-Val677 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Beta-Galactosidase, Acid Beta-Galactosidase, Lactase, Elastin Receptor 1, GLB1, ELNR1 |
| Accession # | P16278 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
LRNATQRMFEIDYSRDSFLKDGQPFRYISGSIHYSRVPRFYWKDRLLKMKMAGLNAIQTYVPWNF HEPWPGQYQFSEDHDVEYFLRLAHELGLLVILRPGPYICAEWEMGGLPAWLLEKESILLRSSDPD YLAAVDKWLGVLLPKMKPLLYQNGGPVITVQVENEYGSYFACDFDYLRFLQKRFRHHLGDDVVLF TTDGAHKTFLKCGALQGLYTTVDFGTGSNITDAFLSQRKCEPKGPLINSEFYTGWLDHWGQPHST IKTEAVASSLYDILARGASVNLYMFIGGTNFAYWNGANSPYAAQPTSYDYDAPLSEAGDLTEKYF ALRNIIQKFEKVPEGPIPPSTPKFAYGKVTLEKLKTVGAALDILCPSGPIKSLYPLTFIQVKQHY GFVLYRTTLPQDCSNPAPLSSPLNGVHDRAYVAVDGIPQGVLERNNVITLNITGKAGATLDLLVE NMGRVNYGAYINDFKGLVSNLTLSSNILTDWTIFPLDTEDAVRSHLGGWGHRDSGHHDEAWAHNS SNYTLPAFYMGNFSIPSGIPDLPQDTFIQFPGWTKGQVWINGFNLGRYWPARGPQLTLFVPQHIL MTSAPNTITVLELEWAPCSSDDPELCAVTFVDRPVIGSSVTYDHPSKPVEKRLMPPPPQKNKDSW LDHVVDHHHHHH
|
| Background | β Galactosidase is a lysosomal β Galactosidase that hydrolyzes the terminal β Galactose from Ganglioside and Keratan sulfate. In lysosome, the mature β Galactosidase protein associates with Cathepsin A and Neuraminidase 1 to form the lysosomal multienzyme complex . An alternative splicing at the RNA level of β Galactosidase results a catalytically inactive β Galactosidase that plays an important role in vascular development. Defects of β-galactosidase (GLB1) are the cause of diseases like GM1-gangliosidosis which is a lysosomal storage disease and Morquio Syndrome B that cause patients to have abnormal elastic fibers. More than 100 mutations have been identified for β Galactosidase, which result in different residual activities of the mutant enzymes and a spectrum of symptoms in the two related diseases. |