Recombinant Human Vaccinia-Related Kinase 3/VRK3
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Vaccinia-Related Kinase 3/VRK3 |
| Source: | Human Cells |
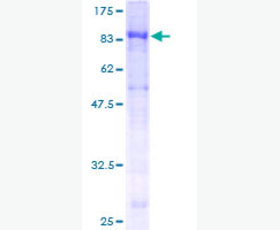
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human Vaccinia-related kinase 3 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Phe412 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Inactive serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK3, Serine/threonine-protein pseudokinase VRK3, Vaccinia-related kinase 3, VRK3 |
| Accession # | Q8IV63-2 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MISFCPDCGKSIQAAFKFCPYCGNSLPVEEHVGSQTFVNPHVSSFQGSKRGLNSSFETSPKKVKW SSTVTSPRLSLFSDGDSSESEDTLSSSERSKGSGSRPPTPKSSPQKTRKSPQVTRGSPQKTSCSP QKTRQSPQTLKRSRVTTSLEALPTGTVLTDKSGRQWKLKSFQTRDNQGILYEAAPTSTLTCDSGP QKQKFSLKLDAKDGRLFNEQNFFQRAAKPLQVNKWKKLYSTPLLAIPTCMGFGVHQDKYRFLVLP SLGRSLQSALDVSPKHVLSERSVLQVACRLLDALEFLHENEYVHGNVTAENIFVDPEDQSQVTLA GYGFAFRYCPSGKHVAYVEGSRSPHEGDLEFISMDLHKGCGPSRRSDLQSLGYCMLKWLYGFLPW TNCLPNTEDIMKQKQKLPWDSFVDHHHHHH
|
| Background | Inactive serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK3 is a 474 amino acids protein that belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, CK1 Ser/Thr protein kinase family and VRK subfamily. It contains a protein kinase domain. VRK3 is widely expressed in human tissues and the protein localizes to the nucleus. VRK3 regulates several transcription factors, nuclear envelope assembly, and chromatin condensation and is also required for cell cycle progression . |