Recombinant Human GMP Reductase 1/GMPR
| Product name: | Recombinant Human GMP Reductase 1/GMPR |
| Source: | Human Cells |
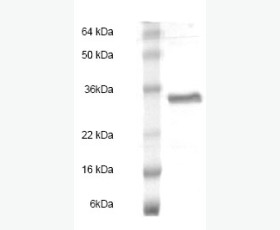
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris-HCl,40% glycerol,0.15M NaCl and 1mM DTT, pH8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human GMP Reductase 1 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Ser345 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | GMP Reductase 1, Guanosine 5'-Monophosphate Oxidoreductase 1, Guanosine Monophosphate Reductase 1, GMPR, GMPR1 |
| Accession # | P36959 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris-HCl,40% glycerol,0.15M NaCl and 1mM DTT, pH8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MPRIDADLKLDFKDVLLRPKRSSLKSRAEVDLERTFTFRNSKQTYSGIPIIVANMDTVGTFEMAA VMSQHSMFTAIHKHYSLDDWKLFATNHPECLQNVAVSSGSGQNDLEKMTSILEAVPQVKFICLDV ANGYSEHFVEFVKLVRAKFPEHTIMAGNVVTGEMVEELILSGADIIKVGVGPGSVCTTRTKTGVG YPQLSAVIECADSAHGLKGHIISDGGCTCPGDVAKAFGAGADFVMLGGMFSGHTECAGEVFERNG RKLKLFYGMSSDTAMNKHAGGVAEYRASEGKTVEVPYKGDVENTILDILGGLRSTCTYVGAAKLK ELSRRATFIRVTQQHNTVFSVDHHHHHH
|
| Background | GMP Reductase 1 (GMPR) is a member of the IMPDH/GMPR family. GMPR exists as a homotetramer and catalyzes the irreversible NADPH-dependent deamination of GMP to IMP. It functions in the conversion of nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide derivatives of G to A nucleotides, and in maintaining the intracellular balance of A and G nucleotides. GMP reductase gene expression may be regulated by MITF. At least two different alleles are known. |