Recombinant Human Lysozyme C/LYZ
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Lysozyme C/LYZ |
| Source: | Human Cells |
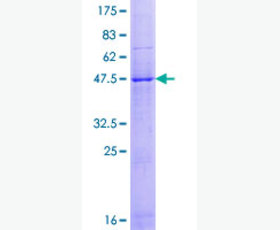
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl,10% Glycerol,pH7.5. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human Lysozyme C is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Lys19-Val148 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Lysozyme C,1,4-beta-N-acetylmuramidase C,LYZ,LZM |
| Accession # | P61626 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl,10% Glycerol,pH7.5. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
KVFERCELARTLKRLGMDGYRGISLANWMCLAKWESGYNTRATNYNAGDRSTDYGIFQINSRYWC NDGKTPGAVNACHLSCSALLQDNIADAVACAKRVVRDPQGIRAWVAWRNRCQNRDVRQYVQGCGV VDHHHHHH
|
| Background | lysozyme C is a secreted protein and belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 22 family. Lysozymes have primarily a bacteriolytic function, damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins. Those in tissues and body fluids are associated with the monocyte-macrophage system and enhance the activity of immunoagents. Lysozyme C is capable of both hydrolysis and transglycosylation; it shows also a slight esterase activity. It acts rapidly on both peptide-substituted and unsubstituted peptidoglycan, and slowly on chitin oligosaccharides. |