Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor IX/F9
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Coagulation Factor IX/F9 |
| Source: | Human Cells |
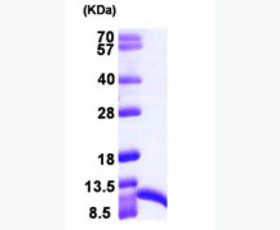
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl,150mM NaCl,10% Glycerol,pH8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human Coagulation factor IX is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Thr29-Thr461 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | F9/Coagulation factor IX/Christmas factor/Plasma thromboplastin component/PTC/Coagulation factor IXa light chain/Coagulation factor IXa heavy chain |
| Accession # | P00740 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl,150mM NaCl,10% Glycerol,pH8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
TVFLDHENANKILNRPKRYNSGKLEEFVQGNLERECMEEKCSFEEAREVFENTERTTEFWKQYVD GDQCESNPCLNGGSCKDDINSYECWCPFGFEGKNCELDVTCNIKNGRCEQFCKNSADNKVVCSCT EGYRLAENQKSCEPAVPFPCGRVSVSQTSKLTRAETVFPDVDYVNSTEAETILDNITQSTQSFND FTRVVGGEDAKPGQFPWQVVLNGKVDAFCGGSIVNEKWIVTAAHCVETGVKITVVAGEHNIEETE HTEQKRNVIRIIPHHNYNAAINKYNHDIALLELDEPLVLNSYVTPICIADKEYTNIFLKFGSGYV SGWGRVFHKGRSALVLQYLRVPLVDRATCLRSTKFTIYNNMFCAGFHEGGRDSCQGDSGGPHVTE VEGTSFLTGIISWGEECAMKGKYGIYTKVSRYVNWIKEKTKLTVDHHHHHH
|
| Background | Coagulation factor IX(F9), is a member of the peptidase S1 family. It contains two EGF-like domains, a Gla domain and a peptidase S1 domain. It is primarily expressed in the liver and secreted in plasma. Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca2+ ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. Mutations in position 43 and 46 prevents cleavage of the propeptide, mutation in position 93 probably fails to bind to cell membranes, mutation in position 191 or in position 226 prevent cleavage of the activation peptide. Mutations of human F9 can result in thrombophilia and recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB). An X-linked blood coagulation disorder characterized by a permanent tendency to hemorrhage, due to factor IX deficiency. It is phenotypically similar to hemophilia A, but patients present with fewer symptoms. Many patients are asymptomatic until the hemostatic system is stressed by surgery or trauma. |