Recombinant Human CTHRC1/NMTC1
| Product name: | Recombinant Human CTHRC1/NMTC1 |
| Source: | Human Cells |
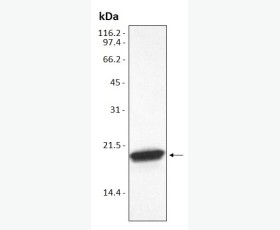
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | Human Cells |
| Description | Recombinant Human CTHRC1 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Ser31-Lys243 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Collagen triple helix repeat-containing protein 1,Protein NMTC1,CTHRC1 |
| Accession # | Q96CG8 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Reconstitution |
Always centrifuge tubes before opening. Do not mix by vortex or pipetting. It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100 μg/ml. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in ddH2O. Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage |
Lyophilized protein should be stored at < -20°C, though stable at room temperature for 3 weeks. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-7°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
SEIPKGKQKAQLRQREVVDLYNGMCLQGPAGVPGRDGSPGANGIPGTPGIPGRDGFKGEKGECLR ESFEESWTPNYKQCSWSSLNYGIDLGKIAECTFTKMRSNSALRVLFSGSLRLKCRNACCQRWYFT FNGAECSGPLPIEAIIYLDQGSPEMNSTINIHRTSSVEGLCEGIGAGLVDVAIWVGTCSDYPKGD ASTGWNSVSRIIIEELPKVDHHHHHH
|
| Background | Collagen triple helix repeat-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTHRC1 gene. It acts as a negative regulator of collagen matrix deposition. It may cause the disease of Barrett esophagus . Patients with Barrett esophagus have an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The main cause of Barrett esophagus is gastroesophageal reflux. The retrograde movement of acid and bile salts from the stomach into the esophagus causes prolonged injury to the esophageal epithelium and induces chronic esophagitis, which in turn is believed to trigger the pathologic changes. |