Recombinant Human Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 5/TRIM5/RNF88
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 5/TRIM5/RNF88 |
| Source: | E. coli |
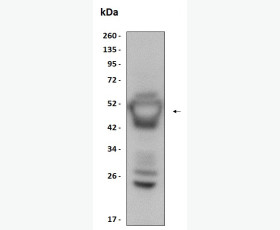
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human TRIM5 is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Gln248 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Names | Tripartite motif-containing protein 5,RING finger protein 88,TRIM5,RNF88 |
| Accession # | Q9C035 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHHSSGLVPRGSHMASGILVNVKEEVTCPICLELLTQPLSLDCGHSFCQACLTANHKK SMLDKGESSCPVCRISYQPENIRPNRHVANIVEKLREVKLSPEGQKVDHCARHGEKLLLFCQEDG KVICWLCERSQEHRGHHTFLTEEVAREYQVKLQAALEMLRQKQQEAEELEADIREEKASWKTQIQ YDKTNVLADFEQLRDILDWEESNELQNLEKEEEDILKSLTNSETEMVQQTQSLRELISDLEHRLQ GSVMELLQ
|
| Background | Tripartite motif-containing Motif 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM5 gene.It is a 493 amino acids protein that belongs to the TRIM/RBCC family.It contains 1 B box-type zinc finger, 1 B30.2/SPRY domain and 1 RING-type zinc finger. TRIM5 present in the cytoplasm recognizes motifs within the capsid proteins and interferes with the uncoating process, therefore preventing successful reverse transcription and transport to the nucleus of the viral genome. The exact mechanism of action has not been shown conclusively, but capsid protein from restricted viruses is removed by proteasome-dependent degradation |