Recombinant Human Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide 2/CALCB
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide 2/CALCB |
| Source: | E. coli |
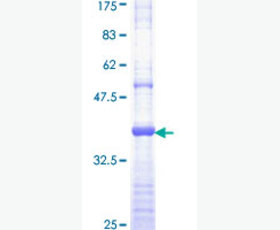
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human CALCB is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Ala127 is expressed with a GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Names | Calcitonin gene-related peptide 2, CALC2, Beta-type CGRP, Calcitonin gene-related peptide II, CALCB. |
| Accession # | P10092 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MSPILGYWKIKGLVQPTRLLLEYLEEKYEEHLYERDEGDKWRNKKFELGLEFPNLPYYIDGDVKL TQSMAIIRYIADKHNMLGGCPKERAEISMLEGAVLDIRYGVSRIAYSKDFETLKVDFLSKLPEML KMFEDRLCHKTYLNGDHVTHPDFMLYDALDVVLYMDPMCLDAFPKLVCFKKRIEAIPQIDKYLKS SKYIAWPLQGWQATFGGGDHPPKSDLVPRGSENLYFQGHMGFRKFSPFLALSILVLYQAGSLQAA PFRSALESSPDPATLSKEDARLLLAALVQDYVQMKASELKQEQETQGSSSAAQKRACNTATCVTH RLAGLLSRSGGMVKSNFVPTNVGSKAFGRRRRDLQA
|
| Background | CALCB is a member of the calcitonin family. CALCB is produced in both peripheral and central neurons. It is a potent peptide vasodilator and can function in the transmission of pain. In the spinal cord, the function and expression of CGRP may differ depending on the location of synthesis. CALCB is derived mainly from the cell bodies of motor neurons when synthesized in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and may contribute to the regeneration of nervous tissue after injury. |