Recombinant Human Cytochrome C/CYCS
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Cytochrome C/CYCS |
| Source: | E. coli |
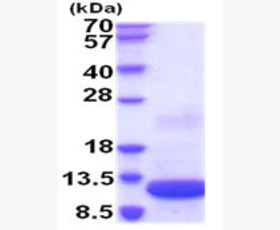
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 20% Glycerol, pH 8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human Cytochrome C is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Gly2-Glu105 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Cytochrome C, CYCS, CYC |
| Accession # | P99999 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 20% Glycerol, pH 8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
GDVEKGKKIFIMKCSQCHTVEKGGKHKTGPNLHGLFGRKTGQAPGYSYTAANKNKGIIWGEDTLM EYLENPKKYIPGTKMIFVGIKKKEERADLIAYLKKATNELEHHHHHH
|
| Background | Cytochrome C (CYCS) is a small heme protein that belongs to the cytochrome c family. It is found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Cytochrome C is a highly soluble protein that functions as a central component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria. CYCS transfers electrons between Complexes III (Coenzyme Q - Cyt C reductase) and IV (Cyt C oxidase). CYCS plays a role in apoptosis. Suppression of the anti-apoptotic members or activation of the pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family leads to altered mitochondrial membrane permeability resulting in release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. Binding of Cytochrome C to Apaf-1 triggers the activation of caspase-9, which then accelerates apoptosis by activating other caspases. |