Recombinant Human α-Crystallin A Chain/CRYAA
| Product name: | Recombinant Human α-Crystallin A Chain/CRYAA |
| Source: | E. coli |
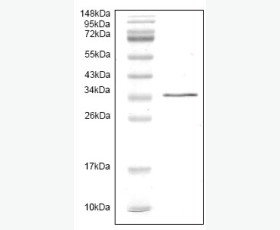
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, 2mM EDTA, pH 8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human alpha-Crystallin A Chain is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Ser173 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Alpha-Crystallin A Chain; Heat Shock Protein Beta-4; HspB4; Alpha-Crystallin A Chain, Short Form; CRYAA; CRYA1; HSPB4 |
| Accession # | P02489 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, 2mM EDTA, pH 8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Reconstitution |
Always centrifuge tubes before opening. Do not mix by vortex or pipetting. It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100 μg/ml. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in ddH2O. Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage |
Lyophilized protein should be stored at < -20°C, though stable at room temperature for 3 weeks. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-7°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MDVTIQHPWFKRTLGPFYPSRLFDQFFGEGLFEYDLLPFLSSTISPYYRQSLFRTVLDSGISEVR SDRDKFVIFLDVKHFSPEDLTVKVQDDFVEIHGKHNERQDDHGYISREFHRRYRLPSNVDQSALS CSLSADGMLTFCGPKIQTGLDATHAERAIPVSREEKPTSAPSSLEHHHHHH
|
| Background | Alpha-Crystallin A Chain (CRYAA) belongs to the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family and can be induced by heat shock. The expression of CRYAA is preferentially restricted to the lens cell. CRYAA may contribute to the transparency and refractive index of the lens. CRYAA has chaperone-like activity, preventing aggregation of various proteins under a wide range of stress conditions. Two additional functions of CRYAA are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. |