Recombinant Human Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Blk/BLK
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Blk/BLK |
| Source: | E. coli |
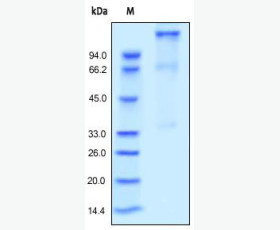
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 1mM DTT, pH 7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human B Lymphocyte Kinase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Gly2-Pro505 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Blk, B Lymphocyte Kinase, p55-Blk, BLK |
| Accession # | P51451 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 1mM DTT, pH 7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
GLVSSKKPDKEKPIKEKDKGQWSPLKVSAQDKDAPPLPPLVVFNHLTPPPPDEHLDEDKHFVVAL YDYTAMNDRDLQMLKGEKLQVLKGTGDWWLARSLVTGREGYVPSNFVARVESLEMERWFFRSQGR KEAERQLLAPINKAGSFLIRESETNKGAFSLSVKDVTTQGELIKHYKIRCLDEGGYYISPRITFP SLQALVQHYSKKGDGLCQRLTLPCVRPAPQNPWAQDEWEIPRQSLRLVRKLGSGQFGEVWMGYYK NNMKVAIKTLKEGTMSPEAFLGEANVMKALQHERLVRLYAVVTKEPIYIVTEYMARGCLLDFLKT DEGSRLSLPRLIDMSAQIAEGMAYIERMNSIHRDLRAANILVSEALCCKIADFGLARIIDSEYTA QEGAKFPIKWTAPEAIHFGVFTIKADVWSFGVLLMEVVTYGRVPYPGMSNPEVIRNLERGYRMPR PDTCPPELYRGVIAECWRSRPEERPTFEFLQSVLEDFYTATERQYELQPLEHHHHHH
|
| Background | Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Blk (BLK) contains one protein kinase domain, one SH2 domain and one SH3 domain. BLK is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, which is involved in B-lymphocyte development, differentiation and signaling. B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling requires a tight regulation of several protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases, and associated coreceptors. Signaling through BLK plays an important role in transmitting signals through surface immunoglobulines and supports the pro-B to pre-B transition, as well as the signaling for growth arrest and apoptosis downstream of B-cell receptor. Defects in BLK are a cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 11 (MODY11). |