Recombinant Human Catalase/CAT
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Catalase/CAT |
| Source: | E. coli |
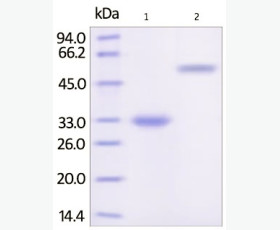
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E. coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human Catalase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Ala2-Leu527 is expressed. |
| Names | Catalase, CAT |
| Accession # | P04040 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB,150mM NaCl,pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
ADSRDPASDQMQHWKEQRAAQKADVLTTGAGNPVGDKLNVITVGPRGPLLVQDVVFTDEMAHFDR ERIPERVVHAKGAGAFGYFEVTHDITKYSKAKVFEHIGKKTPIAVRFSTVAGESGSADTVRDPRG FAVKFYTEDGNWDLVGNNTPIFFIRDPILFPSFIHSQKRNPQTHLKDPDMVWDFWSLRPESLHQV SFLFSDRGIPDGHRHMNGYGSHTFKLVNANGEAVYCKFHYKTDQGIKNLSVEDAARLSQEDPDYG IRDLFNAIATGKYPSWTFYIQVMTFNQAETFPFNPFDLTKVWPHKDYPLIPVGKLVLNRNPVNYF AEVEQIAFDPSNMPPGIEASPDKMLQGRLFAYPDTHRHRLGPNYLHIPVNCPYRARVANYQRDGP MCMQDNQGGAPNYYPNSFGAPEQQPSALEHSIQYSGEVRRFNTANDDNVTQVRAFYVNVLNEEQR KRLCENIAGHLKDAQIFIQKKAVKNFTEVHPDYGSHIQALLDKYNAEKPKNAIHTFVQSGSHLAA REKANL
|
| Background | Catalase (CAT) is a member of the catalase family. It exists as a homotetramer that occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. Catalase is localized in the peroxisome. Catalase promotes growth of cells including T-cells, B-cells, myeloid leukemia cells, melanoma cells, mastocytoma cells, and normal and transformed fibroblast cells. Defects in CAT are the cause of acatalasemia which is characterized by absence of catalase activity in red cells and is associated with ulcerating oral lesions. |