Recombinant Human GDP-L-Fucose Synthase/TSTA3/SDR4E1
| Product name: | Recombinant Human GDP-L-Fucose Synthase/TSTA3/SDR4E1 |
| Source: | E.coli |
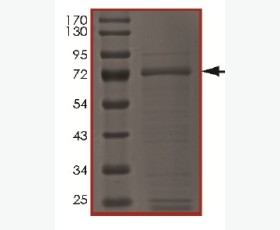
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human GDP-L-Fucose Synthase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Lys321 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | GDP-L-Fucose Synthase, GDP-4-Keto-6-Deoxy-D-Mannose-3,5-Epimerase-4-Reductase, Protein FX, Red Cell NADP(H)-Binding Protein, Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase Family 4E Member 1, TSTA3, SDR4E1 |
| Accession # | Q13630 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MGEPQGSMRILVTGGSGLVGKAIQKVVADGAGLPGEDWVFVSSKDADLTDTAQTRALFEKVQPTH VIHLAAMVGGLFRNIKYNLDFWRKNVHMNDNVLHSAFEVGARKVVSCLSTCIFPDKTTYPIDETM IHNGPPHNSNFGYSYAKRMIDVQNRAYFQQYGCTFTAVIPTNVFGPHDNFNIEDGHVLPGLIHKV HLAKSSGSALTVWGTGNPRRQFIYSLDLAQLFIWVLREYNEVEPIILSVGEEDEVSIKEAAEAVV EAMDFHGEVTFDTTKSDGQFKKTASNSKLRTYLPDFRFTPFKQAVKETCAWFTDNYEQARKLEHH HHHH
|
| Background | GDP-L-Fucose Synthase is a NADP(H)-binding protein. It catalyzes the two-step epimerase and the reductase reactions in GDP-D-mannose metabolism, converting GDP-4-keto-6-D-dexoymannose to GDP-L-fucose. GDP-L-Fucose is the substrate of several fucosyltransferase, involving the expression of mamy glycoconjugates, including blood group ABH antigens and development adhesion antigens. Mutations in the TSTA3 gene may cause leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II. |