Recombinant Human Glutathione Synthetase/GSH Synthetase
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Glutathione Synthetase/GSH Synthetase |
| Source: | E.coli |
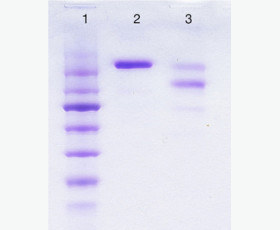
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 200mM NaCl, pH 7.5 . |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human GSH Synthetase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Ala2-Val474 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Names | Glutathione Synthetase, GSH Synthetase, GSH-S, Glutathione Synthase, GSS |
| Accession # | P48637 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 200mM NaCl, pH 7.5 . |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
ATNWGSLLQDKQQLEELARQAVDRALAEGVLLRTSQEPTSSEVVSYAPFTLFPSLVPSALLEQAY AVQMDFNLLVDAVSQNAAFLEQTLSSTIKQDDFTARLFDIHKQVLKEGIAQTVFLGLNRSDYMFQ RSADGSPALKQIEINTISASFGGLASRTPAVHRHVLSVLSKTKEAGKILSNNPSKGLALGIAKAW ELYGSPNALVLLIAQEKERNIFDQRAIENELLARNIHVIRRTFEDISEKGSLDQDRRLFVDGQEI AVVYFRDGYMPRQYSLQNWEARLLLERSHAAKCPDIATQLAGTKKVQQELSRPGMLEMLLPGQPE AVARLRATFAGLYSLDVGEEGDQAIAEALAAPSRFVLKPQREGGGNNLYGEEMVQALKQLKDSEE RASYILMEKIEPEPFENCLLRPGSPARVVQCISELGIFGVYVRQEKTLVMNKHVGHLLRTKAIEH ADGGVAAGVAVLDNPYPVLEHHHHHH
|
| Background | Glutathione Synthetase belongs to the eukaryotic GSH synthase family. Glutathione Synthetase is the second enzyme in the glutathione biosynthesis pathway. It catalyses the condensation of gamma-glutamylcysteine and glycine to form glutathione. Glutathione play an important role in a variety of biological functions, including detoxification of xenobiotics, protection of cells from oxidative damage by free radicals, and membrane transport. The protein functions as a homodimer to catalyze the second step of glutathione biosynthesis, which is the ATP-dependent conversion of gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine to glutathione. Defects in Glutathione Synthetase can also cause the glutathione synthetase deficiency of erythrocytes, which is a mild form causing hemolytic anemia. |