Recombinant Mouse C-C motif chemokine 2/CCL2
| Product name: | Recombinant Mouse C-C motif chemokine 2/CCL2 |
| Source: | E.coli |
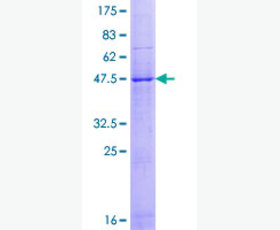
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Mouse C-C motif Chemokine 2 is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Gln24-Arg96 is expressed. |
| Names | C-C motif chemokine 2; Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; Monocyte chemotactic protein 1; MCP-1;Platelet-derived growth factor-inducible protein JE; Small-inducible cytokine A2; Ccl2; Je; Mcp1; Scya2 |
| Accession # | P10148 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Reconstitution |
Always centrifuge tubes before opening. Do not mix by vortex or pipetting. It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100 μg/ml. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in ddH2O. Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage |
Lyophilized protein should be stored at < -20°C, though stable at room temperature for 3 weeks. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-7°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
QPDAVNAPLTCCYSFTSKMIPMSRLESYKRITSSRCPKEAVVFVTKLKREVCADPKKEWVQTYIK NLDRNQMR
|
| Background | C-C motif chemokine 2 (CCL2) is a member of the C-C or β chemokine family. Mouse CCL2 shares 82% amino acid (aa) identity with rat CCL2 over the entire sequence, and 58%, 56%, 55%, 53% and 53% aa identity with human, equine, porcine, bovine and canine CCL2, respectively. Fibroblasts, glioma cells, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes can produce CCL2 either constitutively or upon mitogenic stimulation, but monocytes and macrophages appear to be the major source. In addition to its chemotactic activity, CCL2 induces enzyme and cytokine release by monocytes, NK cells and lymphocytes, and histamine release by basophils that express its receptor, CCR2. Additionally, it promotes Th2 polarization in CD4+ T cells. CCL2-mediated recruitment of monocytes to sites of inflammation is proposed to play a role in the pathology of atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis and allergic asthma. |