Recombinant Human Retinoid-Binding Protein 7
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Retinoid-Binding Protein 7 |
| Source: | E.coli |
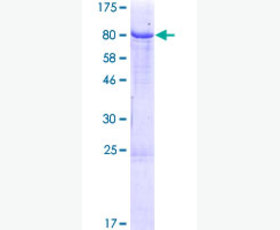
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human Retinoid-binding Protein 7 is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Ala134 is expressed. |
| Names | Retinoid-binding protein 7; Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 4; CRABP4; CRBP4; Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein IV; CRABP-IV; RBP7 |
| Accession # | Q96R05 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Reconstitution |
Always centrifuge tubes before opening. Do not mix by vortex or pipetting. It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100 μg/ml. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in ddH2O. Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage |
Lyophilized protein should be stored at < -20°C, though stable at room temperature for 3 weeks. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-7°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MPADLSGTWTLLSSDNFEGYMLALGIDFATRKIAKLLKPQKVIEQNGDSFTIHTNSSLRNYFVKF KVGEEFDEDNRGLDNRKCKSLVIWDNDRLTCIQKGEKKNRGWTHWIEGDKLHLEMFCEGQVCKQT FQRA
|
| Background | Retinol-binding proteins (RBP) are a family of proteins with diverse functions. They are carrier proteins that bind retinol. Retinol and retinoic acid play crucial roles in the modulation of gene expression and overall development of an embryo. However, deficit or excess of either one of these substances can cause early embryo mortality or developmental malformations. Regulation of transport and metabolism of retinol necessary for a successful pregnancy is accomplished via RBP. Retinol binding proteins have been identified within the uterus, embryo, and extraembryonic tissue of the bovine, ovine, and porcine, clearly indicating that RBP plays a role in proper retinol exposure to the embryo and successful transport at the maternal-fetal interface. |