Recombinant Human Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase/IDO/INDO
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase/IDO/INDO |
| Source: | E.coli |
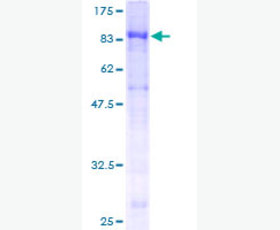
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Sodium Acetate, 150mM NaCl and 20% Glycerol, pH4.5.. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Gly403 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Names | Indole 2,3-dioxygenase, Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1, IDO-1, IDO1, IDO, INDO |
| Accession # | P14902 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM Sodium Acetate, 150mM NaCl and 20% Glycerol, pH4.5.. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/?g (1 IEU/?g) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MNHKVHHHHHHMAHAMENSWTISKEYHIDEEVGFALPNPQENLPDFYNDWMFIAKHLPDLIESGQ LRERVEKLNMLSIDHLTDHKSQRLARLVLGCITMAYVWGKGHGDVRKVLPRNIAVPYCQLSKKLE LPPILVYADCVLANWKKKDPNKPLTYENMDVLFSFRDGDCSKGFFLVSLLVEIAAASAIKVIPTV FKAMQMQERDTLLKALLEIASCLEKALQVFHQIHDHVNPKAFFSVLRIYLSGWKGNPQLSDGLVY EGFWEDPKEFAGGSAGQSSVFQCFDVLLGIQQTAGGGHAAQFLQDMRRYMPPAHRNFLCSLESNP SVREFVLSKGDAGLREAYDACVKALVSLRSYHLQIVTKYILIPASQQPKENKTSEDPSKLEAKGT GGTDLMNFLKTVRSTTEKSLLKEG
|
| Background | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is a heme enzyme that initiates the oxidative degradation of the least abundant, essential amino acid, l-tryptophan, along the kynurenine pathway. This protein is normally expressed in the dendritic cells, macrophages, microglia, eosinophils, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and most tumor cells. IDO activity is associated with immunosuppression and immune attenuation. Several studies showed that IDO can contribute to immune escape when expressed directly in tumor cells or when expressed in immunosuppressive antigen presenting cells such as tolerogenic dendritic cells or tumor associated macrophages. IDO also is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer, chronic viral infections, and other diseases characterized by pathological immune suppression. |