Recombinant Dechloromonas aromatica (Strain RCB) Chlorite Dismutase
| Product name: | Recombinant Dechloromonas aromatica (Strain RCB) Chlorite Dismutase |
| Source: | E.coli |
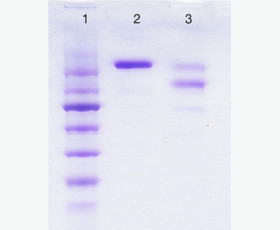
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, 0.5mM EDTA, pH7.4. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Dechloromonas aromatica (strain RCB) Chlorite dismutase Chlorite dismutase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met35-Asp282 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Names | Chlorite dismutase, Chlorite O(2)-lyase, Daro_2580, Cld |
| Accession # | Q47CX0 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, 0.5mM EDTA, pH7.4. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Reconstitution |
Always centrifuge tubes before opening. Do not mix by vortex or pipetting. It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100 μg/ml. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in ddH2O. Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage |
Lyophilized protein should be stored at < -20°C, though stable at room temperature for 3 weeks. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-7°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHHSSGLVPRGSHMENLYFQGMQPMQSMKIERGTILTQPGVFGVFTMFKLRPDWNKVP VAERKGAAEEVKKLIEKHKDNVLVDLYLTRGLETNSDFFFRINAYDLAKAQTFMREFRSTTVGKN ADVFETLVGVTKPLNYISKDKSPGLNAGLSSATYSGPAPRYVIVIPVKKNAEWWNMSPEERLKEM EVHTTPTLAYLVNVKRKLYHSTGLDDTDFITYFETDDLTAFNNLMLSLAQVKENKFHVRWGSPTT LGTIHSPEDVIKALAD
|
| Background | Chlorite dismutase (Cld) found in prokaryotic organisms, also known as Chlorite O2-lyase, is a b-type heme containing enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of chlorite into chloride plus dioxygen. The subunit of chlorite dismutase consists of a heme free N-terminal and a heme b containing C-terminal ferredoxin-like fold with high structural homology to the dye-decolorizing peroxidases (DyPs). The physiological role of Cld in prokaryote has been shown that some microorganisms can use perchlorate or chlorate as terminal electron acceptors for anaerobic respiration thereby producing chlorite that must be detoxified. This enzyme has gained attention because it can be used in the development of bioremediation processes, biosensors, and controlled dioxygen production. |