Recombinant E. coli RNA Pyrophosphohydrolase/rppH
| Product name: | Recombinant E. coli RNA Pyrophosphohydrolase/rppH |
| Source: | E.coli |
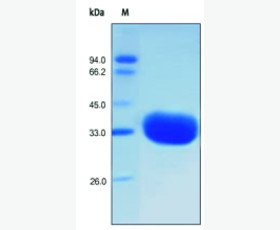
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 50mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH8.0. |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant E.coli RNA pyrophosphohydrolase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Gly176 is expressed. |
| Names | RNA pyrophosphohydrolase, (Di)nucleoside polyphosphate hydrolase, Ap5A pyrophosphatase, rppH |
| Accession # | P0A776 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 50mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH8.0. |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MIDDDGYRPNVGIVICNRQGQVMWARRFGQHSWQFPQGGINPGESAEQAMYRELFEEVGLSRKDV RILASTRNWLRYKLPKRLVRWDTKPVCIGQKQKWFLLQLVSGDAEINMQTSSTPEFDGWRWVSYW YPVRQVVSFKRDVYRRVMKEFASVVMSLQENTPKPQNASAYRRKRG
|
| Background | Messenger RNA (mRNA) degradation plays a key role in the control of gene expression in all organisms by limiting the number of times that each mRNA molecule can be used as a template for protein synthesis. RNA pyrophosphohydrolase, also called RppH, is a master regulator of 5'-dependent mRNA decay. It accelerates the degradation of transcripts by removing pyrophosphate from the 5'-end of triphosphorylated RNA, leading to a more labile monophosphorylated state that can stimulate subsequent ribonuclease cleavage. RppH preferentially hydrolyzes diadenosine penta-phosphate with ATP as one of the reaction products, and can be able to hydrolyze diadenosine hexa- and tetra-phosphate. However, this protein has no activity on diadenosine tri-phosphate, ADP-ribose, NADH and UDP-glucose. In the meningitis causing strain E.coli K1, it has been shown to play a role in HBMEC (human brain microvascular endothelial cells) invasion in vitro. |