Recombinant Human Quinolinate Phosphoribosyltransferase/QPRTase
| Product name: | Recombinant Human Quinolinate Phosphoribosyltransferase/QPRTase |
| Source: | E.coli |
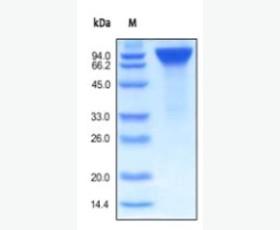
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0 . |
| Applications: | Applications:SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 oC for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 oC for 12 months. |
| UOM: | 100ug/50ug/200ug/1mg/1g |
| Source | E.coli |
| Description | Recombinant Human QAPRTase is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-His297 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Names | Nicotinate-Nucleotide Pyrophosphorylase [Carboxylating], Quinolinate Phosphoribosyltransferase [Decarboxylating], QAPRTase, QPRTase, QPRT |
| Accession # | Q15274 |
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM TrisHCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0 . |
| Shipping |
The product is shipped on dry ice/ice packs. |
| Storage |
Store at < -20°C, stable for 6 months after receipt. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity |
Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin | Less than 0.1 ng/µg (1 IEU/µg) as determined by LAL test. |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
MGSSHHHHHHSSGLVPRGSHMDAEGLALLLPPVTLAALVDSWLREDCPGLNYAALVSGAGPSQAA LWAKSPGILAGQPFFDAIFTQLNCQVSWFLPEGSKLVPVARVAEVRGPAHCLLLGERVALNTLAR CSGIASAAAAAVEAARGAGWTGHVAGTRKTTPGFRLVEKYGLLVGGAASHRYDLGGLVMVKDNHV VAAGGVEKAVRAARQAADFALKVEVECSSLQEAVQAAEAGADLVLLDNFKPEELHPTATVLKAQF PSVAVEASGGITLDNLPQFCGPHIDVISMGMLTQAAPALDFSLKLFAKEVAPVPKIH
|
| Background | Nicotinate-Nucleotide Pyrophosphorylase (QPRT) belongs to the nadC/modD family. QPRT plays an improtant role in catabolism of quinolinate which acts as a potent endogenous exitotoxin to neurons. In addition, QPRT serves as an an intermediate in the Tryptophan-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide pathway. QPRT participates in some pathways including Cofactor biosynthesis, NAD(+) biosynthesis and the Nicotinate D-Ribonucleotide from Quinolinate. In addition, QPRT is involved in the catabolism of Quinolinic Acid (QA). The activity toward QA is slightly repressed by phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) in both a competitive and a non-competitive manner. |