IKBKG antibody
| Product name: | IKBKG antibody |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Purity: | >95% |
| Buffer Formulation: | phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Applications: | WB |
| Storage: | Aliquot and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles |
| UOM: | 100ug |
Rabbit anti-IKBKG polyclonal antibody - N-terminal region
Catalog Number:IC105099
Product Profile
| ProductName | Rabbit anti-IKBKG polyclonal antibody - N-terminal region |
|---|---|
| AntibodyType | Primary Antibodies |
| Immunogen |
The immunogen for anti-IKBKG antibody: synthetic peptide directed towards the N terminal of human IKBKG |
Key Feature
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
|---|---|
| Isotype | IgG |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications | |
| Species Reactivity | |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Purification | Affinity purified |
Target Information
| GeneSymbol | IKBKG |
|---|---|
| GeneSynonyms |
IKBKG
|
| Gene Full Name | Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase gamma |
| Gene Summary |
IKBKG is the regulatory subunit of the IKK core complex which phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B thus leading to the dissociation of the inhibitor/NF-kappa-B complex and ultimately the degradation of the inhibitor. IKBKG also considered to be a mediator for TAX activation of NF-kappa-B. IKBKG could be implicated in NF-kappa-B-mediated protection from cytokine toxicity.Familial incontinentia pigmenti (IP) is a genodermatosis that segregates as an X-linked dominant disorder and is usually lethal prenatally in males (The International Incontinentia Pigmenti Consortium, 2000 [PubMed 10839543]). In affected females it causes highly variable abnormalities of the skin, hair, nails, teeth, eyes, and central nervous system. The prominent skin signs occur in 4 classic cutaneous stages: perinatal inflammatory vesicles, verrucous patches, a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation, and dermal scarring. Cells expressing the mutated X chromosome are eliminated selectively around the time of birth, so females with IP exhibit extremely skewed X-inactivation. Familial incontinentia pigmenti is caused by mutations in the NEMO gene and is here referred to as IP2, or 'classical' incontinentia pigmenti. Sporadic incontinentia pigmenti, the so-called IP1, which maps to Xp11, is categorized as hypomelanosis of Ito (MIM 300337).[supplied by OMIM]. Sequence Note: removed 1 base from the 5' end that did not align to the reference genome assembly. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Entrez Gene record to access additional publications. PRIMARYREFSEQ_SPAN PRIMARY_IDENTIFIER PRIMARY_SPAN COMP 1-2120 AF261086.1 2-2121
More
|
| Alternative Names |
AMCBX1
More
FIP-3 FIP3 Fip3p IKK-gamma IP IP1 IP2 IPD2 NEMO |
| MolecularWeight(MW) | 48kDa |
| Sequence | 419 amino acids |
Database Links
| Entrez Gene | 8517 |
|---|---|
| SwissProt ID | Q9Y6K9 |
| Protein Accession | NP_003630 |
Application
-
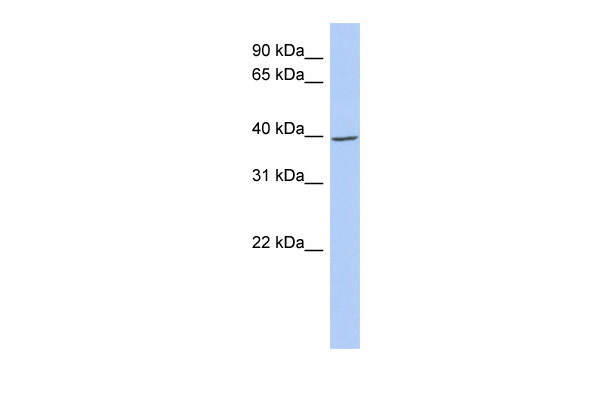
Application
WB Suggested Anti-IKBKG Antibody Titration: 0.2-1 ug/ml
ELISA Titer: 1:62500
Positive Control: Human Spleen
Additional Information
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Storage Instructions | Aliquot and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles |
| Storage Buffer | phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
Note: The product is for research use only,not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
|
|













