Recombinant Lysyl Oxidase (LOX)
| Product name: | Recombinant Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) |
| Source: | Homo sapiens (Human) |
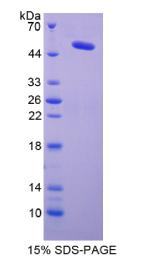
| Purity: | >95% |
| Buffer Formulation: | Supplied as lyophilized form in PBS pH7.4, containing 1mM DTT, 5% trehalose, 0.01% sarcosyl and preservative. |
| Applications: | SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP |
| Storage: | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| UOM: | 50ug/100ug/200ug/1mg |
[ PROPERTIES ]
Residues: Pro213~Tyr417 (Accession # P28300), with two N-terminal Tags, His-tag and GST-tag.
Host: E. coli
Subcellular Location: Secreted, extracellular space.
Purity: >95%
Endotoxin Level: <1.0EU per 1μg (determined by the
LAL method).
Formulation: Supplied as lyophilized form in PBS pH7.4, containing 1mM DTT, 5% trehalose, 0.01% sarcosyl and preservative.
Predicted isoelectric point: 6.2
Predicted Molecular Mass: 50.7kDa
Applications: SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP.
(May be suitable for use in other assays to be determined by the end user.)
[ USAGE ]
Reconstitute in sterile PBS, pH7.2-pH7.4.
[ STORAGE AND STABILITY ]
Storage:Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Store at 2-8oC for one month.
Aliquot and store at -80oC for 12 months.
Stability Test: The thermal stability is described by the loss rate of the target protein. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37oC for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. (Referring from China Biological Products Standard, which was calculated by the Arrhenius equation.) The loss of this protein is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
[ SEQUENCES ]
The target protein is fused with two N-terminal Tags, His-tag and GST-tag, its sequence is listed below.
MSPILGYWKI KGLVQPTRLL LEYLEEKYEE HLYERDEGDK WRNKKFELGL EFPNLPYYID
GDVKLTQSMA IIRYIADKHN MLGGCPKERA EISMLEGAVL DIRYGVSRIA YSKDFETLKV
DFLSKLPEML KMFEDRLCHK TYLNGDHVTH PDFMLYDALD VVLYMDPMCL DAFPKLVCFK
KRIEAIPQID KYLKSSKYIA WPLQGWQATF GGGDHPPKSD GSTSGSGHHH HHHSAGLVPR
GSTAIGMKET AAAKFERQHM DSPDLGTLEV LFQGPLGSEF-PDLVADPY YIQASTYVQK
M S M Y N L R C A A E E N C L A S TAY R A D V R D Y D H R V L L R F P Q R V K N Q G T S D F L P S
R P R Y S W E W H S C H Q H Y H S M D E FS H Y D L L D A N TQ R R VA E G H K AS F C L E D T S C
DYGYHRRFAC TAHTQGLSPG CYDTYGADID CQWIDITDVK PGNYILKVSV NPSYLVPESD
YTNNVVRCDI RYTGHHAYAS GCTISPY
[ REFERENCES ]
1. Haemaelaeinen E.-R., et al. (1991) Genomics 11:508-516.
2. Kim Y., et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:7176-7182.
3. Contente S., et al. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biochem. 194:79-91.
4. Svinarich D.M., et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:14382-14387.